Nutrition for good vision
Nutrition for good vision
The process of seeing takes place In the brain
All information received by the eye is processed in our brain to form an image. In addition, all important control processes also take place in our brain. It is an absolute high-performance organ.
This is reflected in its consumption. Although our brain is only about 2% of our total body weight, it consumes about 20% of the oxygen and 25% of the glucose we take in every day.
It is the control center for all information with a consistently high output.
Our brain processes, coordinates or stores sensory input, feelings, behavior, learning, thinking, speaking, memory, reaction, reflexes in waking and sleeping states. No wonder this unique system in our head requires so much energy.
Our brain is quite complicated. It is the most important organ in humans. It controls not only our body but also our personality.
But it can only do this if we keep it fit by supporting it and making sure that all the nutrients it needs are available.
The most important vitamins for the performance of our brain are:
The provitamin A, the B – vitamins, vitamin C, vitamin K, vitamin D.
Since our brain is 60% fat, it is the fattest organ in our body, so it is important to consume good fats. Omega-3 fatty acids are mainly found in nuts and fatty fish.

Since vision requires a lot of the energy provided by the brain, the same recommendations apply for good visual performance:
1. Beta-carotene or provitamin A.
It is the precursor of vitamin A and is therefore also called provitamin A. Its effects include strengthening memory and ensuring the vitality of neurons, including those we use for vision.
This vitamin is found in orange foods such as carrots and pumpkin, and also in fruits such as melon, papaya and mango.
2. B vitamins are essential for good brain function
Vitamin B1 (thiamine) is abundant in the central and peripheral nervous system. It slows down the aging of the brain. In addition, it is also needed for the visual process.
The vitamin B1 is found in most meats. Especially in beef, pork, chicken and fish. It is also found in nuts, whole grains, fruits and vegetables.
3. Vitamin B6
supports the synthesis of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine, γ-aminobutyric acid, and acetylcholine. Neurotransmitters are responsible for transmitting signals sent by neurons. Vitamin B6 also facilitates the absorption of vitamin B12, which is an important factor in cognitive development.
Vitamin B6 is found in rice, potatoes, white and dark meats, among other foods, as well as eggs, milk and dairy products, seafood, lentils, wheat germ, peppers, and nuts.
4. Vitamin B9 (folic acid or folate)
is another B vitamin needed for the development of the nervous system. Like vitamin B6, it is also required for the synthesis of various neurotransmitters. Vitamin B9 is also involved in the synthesis of red blood cells and thus helps to improve the supply of oxygen to the tissues. In this way, it also supports the work of the brain.
It is found in legumes, whole grains, oats and rice, spinach and asparagus. Bananas, oranges, melons and avocados also contain vitamin B9. Almost all nuts contain vitamin B9, especially peanuts.
5. vitamin B12
plays a major role in amino acid metabolism.
Vitamin B12 is found in beef, white meat, and animal intestines. Also in trout, salmon, shellfish, milk and dairy products, eggs and whole grains.
6. Vitamin C
is a powerful antioxidant. It protects the brain from oxidative stress and degenerative processes thus initiated. Vitamin C helps us absorb iron, and iron is important for our memory and concentration.
This vitamin is found in all citrus fruits and green vegetables.
7. Vitamins D, K and E & Omega-3 fatty acids
There are other vitamins for the brain that are equally important. One of them is vitamin D. We can find this vitamin in sardines, salmon, tuna and other fish, as well as in mushrooms.
Vitamin K contributes to better learning ability and memory.
We can find this vitamin in high concentrations in broccoli. Likewise, it is found in Brussels sprouts, parsley, leafy greens, asparagus, celery and fermented foods.
Last but not least, vitamin E and omega-3 fatty acids are also exceptionally good for the brain. The former is a wonderful antioxidant, while the latter improves neuroplasticity. With both, we are better protected from degenerative processes and sharpen our minds.
Nutrition is a major factor in our quality of life
Health and disease often have to do with how we eat and how we manage ourselves, our energy and our bodies.
Exercise and mental training help us with this. Spending time outdoors and exercising regularly are just as important as mentally challenging and encouraging ourselves. That’s why it’s good to learn new things, be curious and keep mentally fit. Also, it is now proven that mindfulness and meditation have a good impact on our brain performance.
Did you know that Vision Training is also a kind of brain training?
Health and disease often have to do with how we eat and how we manage ourselves, our energy and our bodies.
Exercise and mental training help us with this. Spending time outdoors and exercising regularly are just as important as mentally challenging and encouraging ourselves. That’s why it’s good to learn new things, be curious and keep mentally fit. Also, it is now proven that mindfulness and meditation have a good impact on our brain performance.
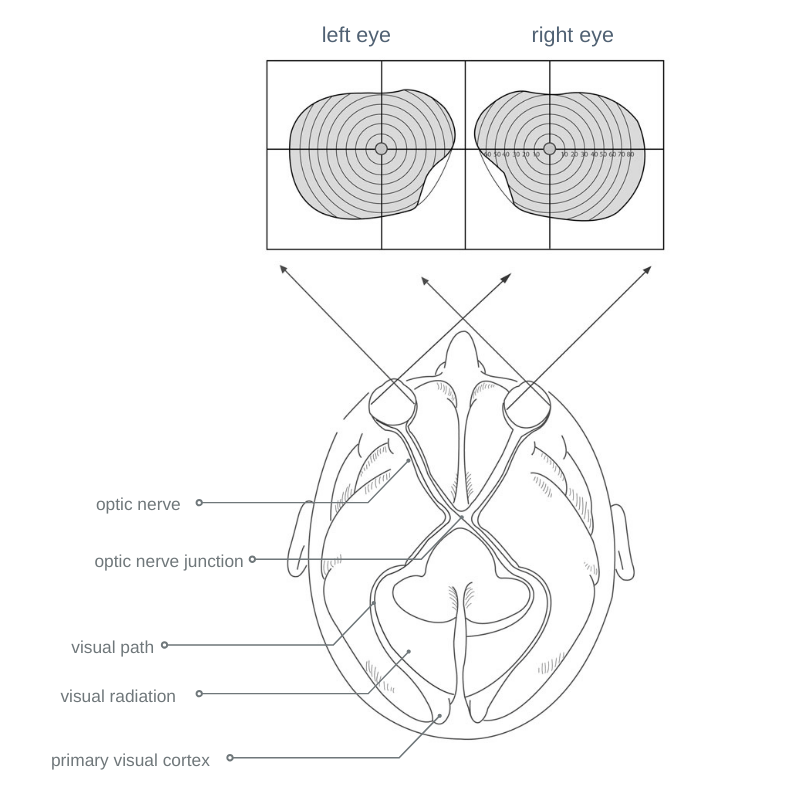
We perceive our environment with our eyes. However, how and what we see does not depend solely on our most important sensory organ. The actual image is created somewhere else – in our brain. And with the help of Vision Training, this can certainly be controlled.
From this perspective, the eye merely catches the raw material and passes it on for processing.
What exactly happens during this process?
Through the interaction of the optical elements of the eyes – cornea, lens and eye fluid – a sharp image is imaged on the retina and converted into energy. It then travels along thin nerve fibers to the optic nerve in the brain, where the nerve tracts branch out.
About two-thirds of the brain is involved in the visual process. Some brain areas are responsible for the recognition of shapes, others for color perception or spatial orientation. Peripheral vision is responsible for the perception of movement. We use this ability primarily when driving a car.
This is a complex process that can be influenced or changed with Vision Training. Not only the physical part of vision is considered, but also the mental and psychological aspects. This means that through repeated visual stimulation we also change the neurophysiological control mechanism. In our brain we have stored past events, feelings and experiences that not only help in the visual process, but can block it and have a negative effect on vision. With the help of Vision Training, this can be uncovered and possibly resolved.
INFORMATION







